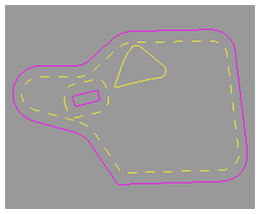
 The exterior boundary marks the perimeter of a field.
The exterior boundary marks the perimeter of a field. The exterior boundary marks the perimeter of a field.
The exterior boundary marks the perimeter of a field.
Interior boundaries mark important areas of the field. Interior boundaries can either be impassable (pink) or passable (yellow). An example of an impassable boundary is a well. An example of a passable boundary is a waterway.
Headland boundaries (yellow dashes) mark areas in the field where there are end rows or turn rows. They are created inside the exterior boundary and around impassable interior boundaries.
When used with Section Control, boundaries prevent application of product inside marked areas of the field and outside of the field.
All active interior boundary areas are subtracted from the exterior boundary area.
An estimated boundary area is calculated on a flat two-dimensional plane. Elevation changes are not used in boundary area calculation.
Work Totals include elevation changes in area worked totals. Due to calculation differences, boundary and work totals vary.
The field associated to the boundary is displayed.
|
Select to edit the boundary name. |
|
|
Displays the exterior boundary for the field. Select to edit the exterior boundary or add a headland to the boundary. |
|
|
Displays the interior boundaries for the field. Select to edit the interior boundaries or add a headland to the impassable boundaries. |
|
|
Autonomy boundaries that are compatible for machine autonomy are indicated with a blue icon. |
|
NOTE: The exterior boundary must meet the autonomy boundary requirements for the boundary to be autonomy compatible.
|
Delete Boundary - Select to delete the selected boundary. |
|
|
Create - Select to create a new exterior boundary. |
|
|
Create Boundary Track - Select to create guidance tracks using the exterior boundary. |
|